Connect Hue to PostgreSQL
If you have an external database installed, review Postgres Troubleshooting before creating a database for Hue.
Continue reading:
Install and Configure PostgreSQL Server
Refer to the PostgreSQL documentation for more help on how to install a PostgreSQL database.
Continue reading:
Postgres Troubleshooting
Pay close attention to these areas and revisit when troubleshooting:
- Python: Some Linux distributions need python-psycopg2 (for PostgreSQL). See the community thread.
- Security: Delete anonymous users because they are able to log on without a password.
- Remote connections: The listen address should be set to 0.0.0.0 so it can listen to multiple hosts.
- Authentication: Configure pg_hba.conf as follows (and change database/user as appropriate):
# TYPE DATABASE USER CIDR-ADDRESS METHOD local all all trust # Remote access host all all 127.0.0.1/32 password # IPv4 host all all ::1/128 password # IPv6 host hue_d hue_u 0.0.0.0/0 md5
- Schemas: For private schemas, configure Django with the schema owner to DROP objects.
Install PostgreSQL Server
- Install and initialize the PostgreSQL server. The table lists the max version of each supported distribution for this CDH release, and corresponding default database versions.
| OS | OS Ver | DB Ver | Command |
|---|---|---|---|
| CentOS / RHEL | 7.3 | 9.2 |
sudo yum install postgresql-server sudo postgresql-setup initdb |
| 6.8 | 8.4 |
sudo yum install postgresql-server sudo service postgresql initdb |
|
| SLES | 12.1, 12.2 | 9.4 |
zypper install postgresql postgresql-server systemctl start postgresql |
| 11.4 | 8.4 |
# Refresh repo for python-psycopg2 zypper addrepo http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/server:database:postgresql/SLE_11_SP4/server:database:postgresql.repo zypper refresh --- zypper install postgresql postgresql-server rcpostgresql start |
|
| Ubuntu | 16.04 | 9.5 |
sudo apt-get install postgresql |
| 14.04 | 9.3 |
sudo apt-get install postgresql |
|
| 12.04 | 9.1 |
sudo apt-get install postgresql |
|
| Debian | 8.4 | 9.4 |
sudo apt-get install postgresql |
| 7.8 | 9.1 |
sudo apt-get install postgresql |
 Tip: If you need to start over, you can reinitialize:
Tip: If you need to start over, you can reinitialize:
rm -rf /var/lib/pgsql/* <reinitialize per your os>
Configure PostgreSQL Server
- Configure pg_hba.conf to set authentication
methods:
# TYPE DATABASE USER CIDR-ADDRESS METHOD local all all trust # Remote access host all all 127.0.0.1/32 password # IPv4 host all all ::1/128 password # IPv6 host hue_d hue_u 0.0.0.0/0 md5
- CentOS/RHEL/SLES : /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf:
vi /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf
- Ubuntu/Debian: /etc/postgresql/<pgres version>/main/pg_hba.conf:
vi /etc/postgresql/`ls -l /etc/postgresql | tail -1 | awk '{print $9}'`/main/pg_hba.conf
- CentOS/RHEL/SLES : /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf:
- Configure postgresql.conf to listen to
all available addresses:
listen_addresses = '0.0.0.0'
- CentOS/RHEL/SLES: /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf
vi /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf
- Ubuntu/Debian: /etc/postgresql/<version>/main/postgresql.conf:
vi /etc/postgresql/`ls -l /etc/postgresql | tail -1 | awk '{print $9}'`/main/postgresql.conf
- CentOS/RHEL/SLES: /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf
- Start (or restart) the database and enable automatic start on boot if necessary.
Table 2. Restart Commands OS OS Ver Command CentOS / RHEL 7.3 sudo systemctl restart postgresql sudo systemctl enable postgresql
6.8 sudo service postgresql restart sudo chkconfig postgresql on sudo chkconfig postgresql --list
SLES 12.1, 12.2 systemctl restart postgresql
11.4 rcpostgresql restart
Ubuntu 12.04, 14.04, 16.04 sudo /etc/init.d/postgresql restart
Debian 7.8, 8.4 sudo /etc/init.d/postgresql restart
Create Hue Database
 Important: If you use a private schema, you must configure Django to use the schema
owner (which can be a user or group) to DROP objects, because DROP is not a grantable permission in
postgreSQL.
Important: If you use a private schema, you must configure Django to use the schema
owner (which can be a user or group) to DROP objects, because DROP is not a grantable permission in
postgreSQL.- Create the hue_d database and grant privileges to the hue_u user:
sudo -u postgres psql postgres=# create database hue_d with lc_collate='en_US.UTF-8'; CREATE DATABASE postgres=# create user hue_u with password 'huepassword'; CREATE ROLE postgres=# grant all privileges on database hue_d to hue_u; GRANT
 Note: You can name the Hue database and user anything you like.
Note: You can name the Hue database and user anything you like. - Verify the connection to the hue_d database.
psql -h localhost -U hue_u -d hue_d Password for user hue_u: hue=> \q
 Note: If you cannot connect, try typing the command manually. The hyphens may become corrupted when
copied.
Note: If you cannot connect, try typing the command manually. The hyphens may become corrupted when
copied.
Connect Hue Service to PostgreSQL
 Tip: To save the data in your current database (embedded or external), you must migrate (dump, synch,
load) before connecting to the new database. Otherwise, skip those steps.
Tip: To save the data in your current database (embedded or external), you must migrate (dump, synch,
load) before connecting to the new database. Otherwise, skip those steps.- Stop Hue Service
- In Cloudera Manager, navigate to .
- Select .
 Note: If necessary, refresh the page to ensure the Hue service is stopped:
Note: If necessary, refresh the page to ensure the Hue service is stopped:  .
.
- [migration only] Dump Current Database
- Select .
- Click Dump Database. The file is written to /tmp/hue_database_dump.json on the host of the Hue server.
- Log on to the host of the Hue server in a command-line terminal.
- Edit /tmp/hue_database_dump.json by removing all objects with useradmin.userprofile in the
model field. For example:
# Count number of objects grep -c useradmin.userprofile /tmp/hue_database_dump.json
vi /tmp/hue_database_dump.json
{ "pk": 1, "model": "useradmin.userprofile", "fields": { "last_activity": "2016-10-03T10:06:13", "creation_method": "HUE", "first_login": false, "user": 1, "home_directory": "/user/admin" } }, { "pk": 2, "model": "useradmin.userprofile", "fields": { "last_activity": "2016-10-03T10:27:10", "creation_method": "HUE", "first_login": false, "user": 2, "home_directory": "/user/alice" } },
- Connect to New Database
- Go to .
- Filter by category, Database.
- Set the following database parameters :
DB Hostname = <fqdn of host with postgres server>:5432 DB Type = <PostgreSQL> DB Name = hue_d Username = hue_u Password = <hue database password set when granting hue permissions>
- Click Save Changes.
- [migration only] Synchronize New Database
- Select
- Click Synchronize Database.
- [migration only] Load Data from Old Database
- Log on to the host of the PostgreSQL server in a command-line terminal.
psql -h localhost -U hue_u -d hue_d Password for user hue_u: <hue user password>
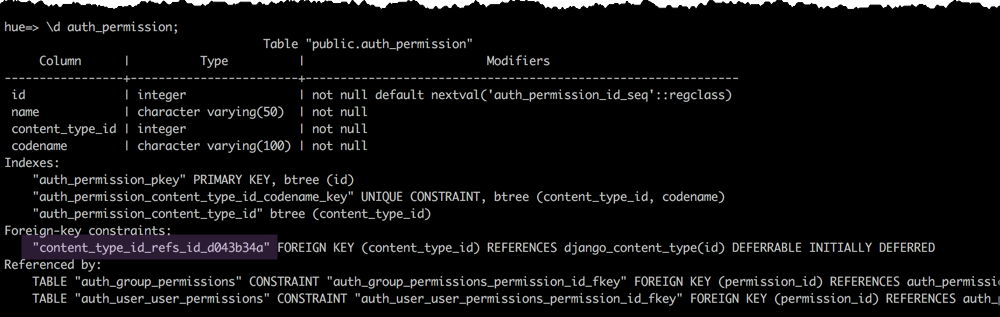
- Drop the foreign key constraint from the auth_permission table in the hue database.
hue=# \d auth_permission; hue=# ALTER TABLE auth_permission DROP CONSTRAINT content_type_id_refs_id_id value;
- Clean the table, django_content_type.
hue=# TRUNCATE django_content_type CASCADE;
- In Cloudera Manager, load the JSON file: select and
click Load Database.
 Tip: If you are blocked by a duplicate key value such as this:
Tip: If you are blocked by a duplicate key value such as this:
django.db.utils.IntegrityError: Problem installing fixture '/tmp/hue_database_dump.json': Could not load desktop.DocumentTag(pk=1): duplicate key value violates unique constraint "desktop_documenttag_owner_id_1d5f76680ee9998b_uniq" DETAIL: Key (owner_id, tag)=(1100713, default) already exists.
Delete that value and try loading again, for example:DELETE FROM desktop_documenttag WHERE owner_id = '1100713' and tag = 'default';
- Add the foreign key back (still logged on to the Hue database):
ALTER TABLE auth_permission ADD FOREIGN KEY (content_type_id) REFERENCES django_content_type (id);
- Log on to the host of the PostgreSQL server in a command-line terminal.
- Start Hue service
- Navigate to , if not already there.
- Select .
- Click Start.
- Click Hue Web UI to log on to Hue with a custom PostgreSQL database.
Page generated July 25, 2018.
| << Connect Hue to MySQL or MariaDB | ©2016 Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved | Connect Hue to Oracle with Client Parcel >> |
| Terms and Conditions Privacy Policy |