Connect Hue to MySQL or MariaDB
If you have an external database installed, review MySQL/MariaDB Troubleshooting before creating a database for Hue.
Continue reading:
Install and Configure MySQL or MariaDB Server
MariaDB is a fork of the MySQL relational database. Refer to the MariaDB documentation or MySQL documentation for more help on how to install a MariaDB or MySQL database.
Continue reading:
MySQL/MariaDB Troubleshooting
Pay close attention to these areas and revisit when troubleshooting:
- Remote connections:
- The bind or address should be set to 0.0.0.0 so it can listen to multiple hosts.
- Grant wildcard (%) permissions to the Hue database user so it can connect from any host.
- Install a JDBC connector if necessary, for example, if your CDH version does not include it.
- Security: Delete anonymous users because they are able to log on without a password.
- Storage engine: Use InnoDB (the default engine in version 5.5.5 and higher: mysql -V).
- Data validation: Use sql_mode=STRICT_ALL_TABLES to prevent columns being truncated during migration.
Install MySQL or MariaDB Server
- Install MariaDB or MySQL. The table lists the max version of each supported distribution for this CDH release, and corresponding default database versions.
Table 1. Install Commands for Supported OS Versions OS OS Ver DB Ver Command CentOS / RHEL
7.3 No package mysql-server available. 5.5 sudo yum install mariadb-server
6.8 5.1 sudo yum install mysql-server
No package mariadb-server available. SLES 12.2 'mysql' not found in package names. 10.0 sudo zypper install mariadb
11.4 5.5 sudo zypper install mysql
'mariadb' not found in package names. Ubuntu 16.04 5.7 sudo apt-get install mysql-server #set root psswd when prompted
10.0 sudo apt-get install mariadb-server #set root psswd when prompted
14.04 5.5 sudo apt-get install mysql-server #set root psswd when prompted
5.5 sudo apt-get install mariadb-server #set root psswd when prompted
12.04 5.5 sudo apt-get install mysql-server #set root psswd when prompted
Unable to locate package mariadb-server Debian 8.4 5.5 sudo apt-get install mysql-server #set root psswd when prompted
10.0 sudo apt-get install mariadb-server #set root psswd when prompted
7.8 5.5 sudo apt-get install mysql-server #set root psswd when prompted
Package 'mariadb-server' has no installation candidate - Start the database server as necessary (some are automatically started):
Table 2. Start Commands OS OS Ver Command CentOS / RHEL 7.3 sudo systemctl start mariadb
6.8 sudo service mysqld start
SLES 11.4, 12.1, 12.2 sudo rcmysql start
Ubuntu 12.04, 14.04, 16.04 sudo service mysql start
Debian 7.8, 8.4 sudo service mysql start
- Secure your installation. If you make a mistake, simply rerun:
sudo /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
Enter current password for root (enter for none): [If unset, press Enter.] OK, successfully used password, moving on... [...] Set root password? [Y/n] Y [Enter n if password is set.] New password: Re-enter new password: Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y [...] Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] N [...] Remove test database and access to it [Y/n] Y [...] Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
Configure MySQL or MariaDB Server
- Configure my.cnf (only as necessary).
- Ensure bind-address=0.0.0.0 (or is commented out if the default).
- Ensure default-storage-engine=innodb (which is the default in 5.5 and higher: mysql -V).
- Ensure sql_mode=STRICT_ALL_TABLES to avoid columns being truncated during migration.
[mysqld] ... bind-address=0.0.0.0 default-storage-engine=innodb sql_mode=STRICT_ALL_TABLES
- CentOS/RHEL/SLES: /etc/my.cnf
-
Ubuntu/Debian: /etc/mysql/my.cnf
- Restart the database server.
 Note: See the Start Commands table above and replace with "restart".
Note: See the Start Commands table above and replace with "restart". - Enable the server to automatically start on boot:
Table 3. Enable Automatic Start OS OS Ver Command CentOS / RHEL 7.3 sudo systemctl enable mariadb
6.8 sudo chkconfig mysqld on
SLES 11.4, 12.1, 12.2 sudo chkconfig mysql on sudo rcmysql status
Ubuntu 12.04, 14.04, 16.04 # preconfigured to start at boot sudo service mysql status
Debian 7.8, 8.4 # preconfigured to start at boot sudo service mysql status
Create Hue Database
- Log on to MySQL or MariaDB with your root password:
mysql -u root -p Enter password: <root password>
- Create a database for Hue (we call it "hue" but any name works) with UTF8 collation and grant user privileges:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE hue DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 DEFAULT COLLATE utf8_general_ci; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON hue.* TO 'hue'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '<password>'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
- Verify the connection to the Hue database:
mysql -u hue -p Enter password: <password> quit
 Note:
Note:
Ensure Hue uses UTF8 collation and character set. Some commands:
# To create (use utf8_general_ci or utf8mb4_general_ci): CREATE DATABASE hue COLLATE = 'utf8_general_ci'; # To view default_character_set_name and default_collation_name SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.SCHEMATA; # To alter if not created with UTF8 collation ALTER DATABASE hue COLLATE = 'utf8_general_ci';See Setting Character Sets and Collations.
Connect Hue Service to MySQL
 Tip: To save the data in your current database (embedded or external), you must migrate (dump, synch,
load) before connecting to the new database. Otherwise, skip those steps.
Tip: To save the data in your current database (embedded or external), you must migrate (dump, synch,
load) before connecting to the new database. Otherwise, skip those steps.- Stop Hue Service
- In Cloudera Manager, navigate to .
- Select .
 Note: Refresh the page if the Hue service does not look stopped:
Note: Refresh the page if the Hue service does not look stopped:  .
.
- [migration only] Dump Current Database
- Select .
- Click Dump Database. The file is written to /tmp/hue_database_dump.json on the host of the Hue server.
- Log on to the host of the Hue server in a command-line terminal.
- Edit /tmp/hue_database_dump.json by removing all objects with useradmin.userprofile in the
model field. For example:
# Count number of objects grep -c useradmin.userprofile /tmp/hue_database_dump.json
vi /tmp/hue_database_dump.json
{ "pk": 1, "model": "useradmin.userprofile", "fields": { "last_activity": "2016-10-03T10:06:13", "creation_method": "HUE", "first_login": false, "user": 1, "home_directory": "/user/admin" } }, { "pk": 2, "model": "useradmin.userprofile", "fields": { "last_activity": "2016-10-03T10:27:10", "creation_method": "HUE", "first_login": false, "user": 2, "home_directory": "/user/alice" } },
- Connect to New Database
- Go to .
- Filter by category, Database.
- Set the following database parameters:
- Hue Database Type: MySQL
- Hue Database Hostname: FQDN of host running MySQL server
- Hue Database Port: 3306,5432, or 1521
- Hue Database Username: username
- Hue Database Password: password
- Hue Database Name: Hue database name or SID
- Click Save Changes.
- [migration only] Synchronize New Database
- Select
- Click Synchronize Database.
- [migration only] Load Data from Old Database
- Log on to the host of the MySQL server in a command-line terminal.
mysql -u root -p Enter password: <root password>
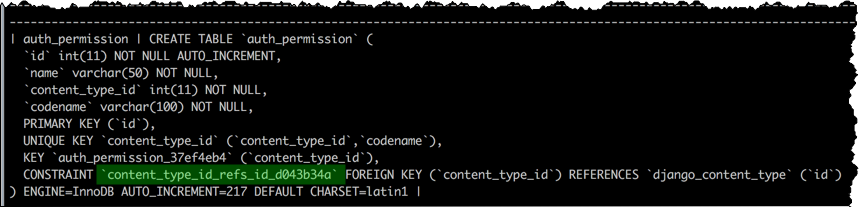
- Drop the foreign key constraint from the auth_permission table in the hue database.
SHOW CREATE table hue.auth_permission; ALTER TABLE hue.auth_permission DROP FOREIGN KEY content_type_id_refs_id_id value;
- Clean the table, django_content_type.
DELETE FROM hue.django_content_type;
- In Cloudera Manager, load the JSON file: select and click Load Database.
- Add the foreign key back:
ALTER TABLE hue.auth_permission ADD FOREIGN KEY (content_type_id) REFERENCES django_content_type (id);
- Log on to the host of the MySQL server in a command-line terminal.
- Start Hue service
- Navigate to , if not already there.
- Select .
- Click Start.
- Click Hue Web UI to log on to Hue with a custom MySQL database.
Page generated July 25, 2018.
| << Hue Custom Databases | ©2016 Cloudera, Inc. All rights reserved | Connect Hue to PostgreSQL >> |
| Terms and Conditions Privacy Policy |